Grade 1 osteochondrosis of the cervical spine is the initial stage of irreversible destructive and degenerative changes occurring in the cartilaginous intervertebral discs and the bone bodies of the vertebrae.It is rarely possible to diagnose the pathology in the early stages of development, since cervical osteochondrosis does not necessarily manifest itself clinically.Even on X-rays, characteristic signs of damage to cartilaginous structures are often absent.
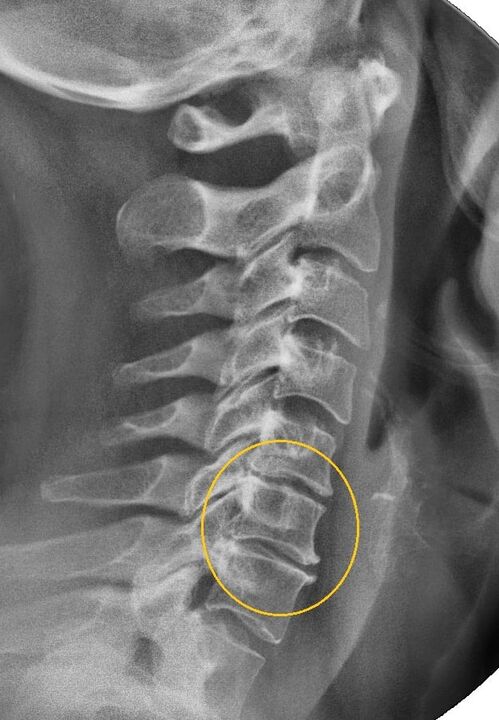
Features of 1st degree cervical osteochondrosis
Grade 1 osteochondrosis of the cervical spine is often detected accidentally - during the diagnosis of other pathologies, even if they are not related to the musculoskeletal system.But sometimes the patient himself visits the doctor because of the deterioration of his general health.In fact, despite the absence of pronounced symptoms of osteochondrosis, the intervertebral discs have already undergone degenerative changes:
- cartilaginous tissues become denser and expanded;
- radial cracks appeared on the fibrous rings.
The loss of tightness and elasticity of the intervertebral discs impaired their shock-absorbing properties.Because they are unable to fully relieve the load on the vertebrae, mild instability of the cervical spine still occurs.But even a slight displacement of cartilage or bone structures is a prerequisite for further rapid progression of osteochondrosis.
Clinical picture
With grade 1 osteochondrosis of the cervical spine, the characteristic signs of this pathology may be absent.A person explains the discomfort that occurs from time to time due to fatigue after physical activity or muscle tension, because the body is in one position for a long time.The intensity of the pain in the back of the neck gradually increases.
Intermittent, aching and still mildly expressed painful sensations first appear after lifting heavy objects or hypothermia.They do not have a clear localization, they often radiate to the shoulders and upper back.A shoulder pain syndrome develops, which will be the first specific sign of cervical osteochondrosis.At the initial stage of development, the pathology can be clinically manifested as follows:
- limited mobility in the neck.When tilting or turning the head, the stiffness of the movements is felt, there is no pain;
- The sensitivity of the parts of the body innervated by common nerve plexuses in the neck region begins to decrease.Palpation of the shoulder and forearm decreases, less often the hands;
- the patient feels that the muscle strength of the arm is decreasing;
- Headaches and dizziness become more frequent, visual acuity decreases for a short time.


Cervical osteochondrosis of the 1st degree may refer to attacks of acute, piercing, shooting pain.They usually occur when the head suddenly turns.This is how the increased tone of the neck muscles is manifested.Their spasms are the body's compensatory reaction to the instability of the spinal segments.
Alternating relapses with phases of remission are characteristic of osteochondrosis.During exacerbations, a constant discomfort is felt in the neck.The clinical picture includes vascular, neurological and static signs at the same time.In the remission stage, the disease is practically asymptomatic.
Diagnostics
The diagnosis is made based on the patient's complaints and a series of tests to determine the mobility of the neck segments.The clue is a medical history of previous injuries or systemic pathologies of the skeletal muscle system (gout, rheumatic, reactive arthritis).
The most informative diagnostic procedure is radiography.Grade 1 pathologies correspond to radiological stage 1 or 2.The resulting images show the typical signs of the disease.
| X-ray stages of 1st degree cervical osteochondrosis | Characteristic signs |
|---|---|
| Section 1 | Minor changes in the curvature of the spine in the cervical region, affecting one or more segments |
| Section 2 | Slight thickening of intervertebral discs, deformation of uncinate processes, straightening of lordosis, minor growth of bone structures |
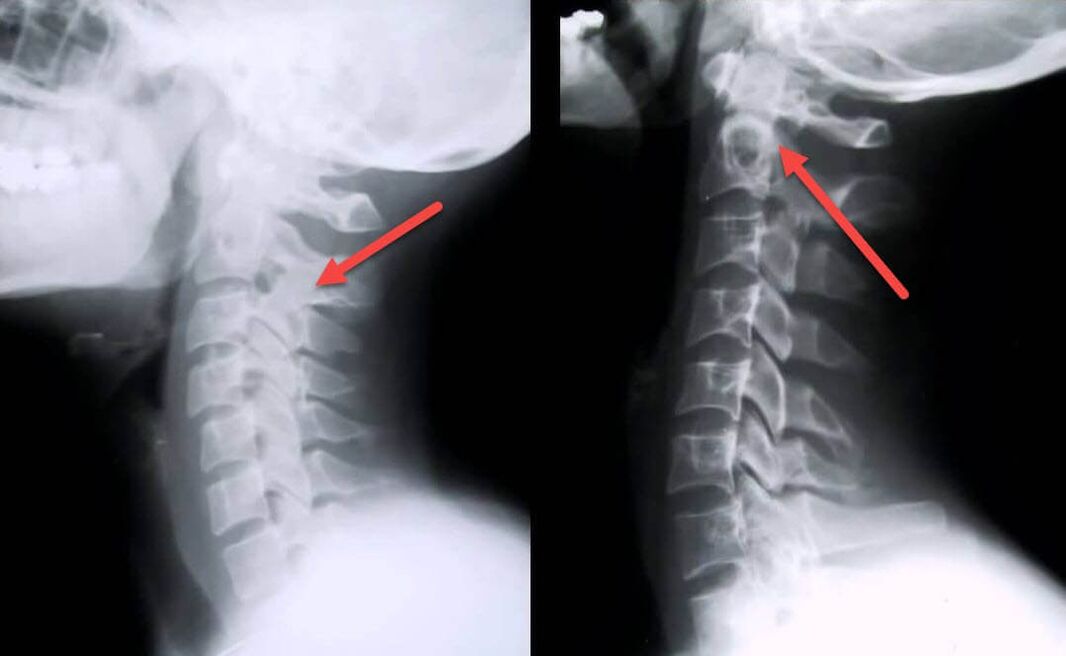
Magnetic resonance imaging is sometimes required to clarify the diagnosis.With its help, you can detect an aseptic, sluggish inflammatory process and destructive-degenerative changes in the intervertebral discs.
Therapy
The treatment of grade 1 cervical osteochondrosis is long-term.At the initial stage of development, the pathology responds well to conservative therapy.Patients are prescribed medication and recommended physiotherapy and massage treatments.

All treatment methods are aimed at improving the blood circulation of the cervical spine.This allows you to avoid the deterioration of the trophism of the intervertebral discs - this is the main reason for the development of osteochondrosis.Eliminating the lack of nutrients and oxygen stimulates the partial regeneration of the cartilage tissue.
Pharmacological drugs
Clinically, grade 1 osteochondrosis is manifested by mild pain, the elimination of which does not require the use of drugs in the form of tablets or solutions intended for parenteral administration.If necessary, patients are recommended to rub ointments, gels or creams into the back of the neck:
- non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs;
- local irritating, disturbing, heating agents.
In this case, it is even better to use biologically active additives for external use, such as camphor, ant alcohol, red pepper extract, and bee venom, rather than medicines.
Vertebrologists include systemic chondroprotectors in therapeutic regimens.Injection solutions are used for several days.After that, the therapeutic effect is consolidated by taking the tablets.The duration of the treatment lasts from several months to 2 years.
It is not a drug treatment
For the treatment of osteochondrosis of the 1st degree, physiotherapy methods are used using various physical factors: low-frequency currents, magnetic fields, laser, ultrasound.The procedures help to relieve pain, relieve aseptic inflammation and eliminate increased tone of the neck muscles.
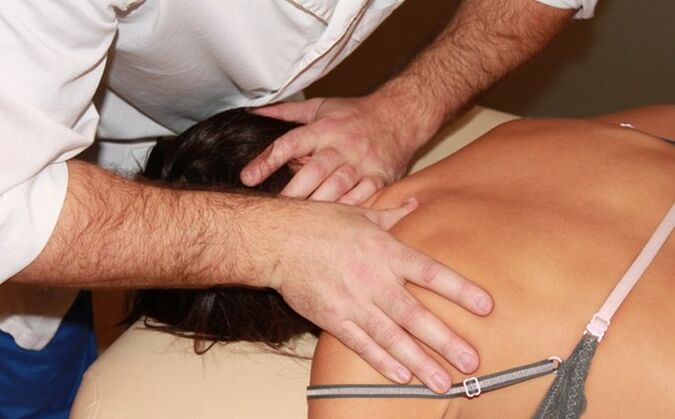
Neurologists and vertebrologists recommend that patients regularly visit the massage room.Thanks to the dosed mechanical effect on the vertebrae, spasmodic muscles relax, blood circulation and microcirculation improve, and local immunity is strengthened.The following massage types are used in the treatment of cervical osteochondrosis:
- classic;
- point;
- vacuum.
Manual therapy with an individually selected effect method allows increasing the range of motion of the cervical spine and eliminating the first signs of lordosis changes.
To restore the anatomically correct shape of the spine or to increase the distance between the vertebrae, traction (dry or underwater traction of the spine) is used.
Regular exercise therapy can replace medication, massage and physiotherapy.During exercise therapy, blood circulation improves, the neck muscles that stabilize the vertebrae are strengthened, and tissue trophism is normalized.Daily training is excellent for preventing pain and movement stiffness.
The first physical therapy (kinesitherapy) classes are conducted under the guidance of a physical therapist.It shows how to perform exercises, dosing the load on the discs and vertebrae to avoid compression of the spinal roots.After a few days, the patient can exercise independently at home.
The value of timely recognition of the disease lies in the favorable prognosis of complete recovery.The sooner the therapy is carried out, the greater the probability of a complete restoration of the functional activity of the spinal column.



















